NodeJS - Build a LiveView
Since you've already downloaded the LiveViewJS repo, it should be easy to create a new LiveView and add it to your webserver. Let's get started!
Create a new LiveView in Express
Since we are using Express to serve our LiveViews, we'll create a new LiveView in the packages/express directory.
Use your favorite editor to create a new file packages/express/src/example/liveview/hello.ts and add the following
code and hit save:
import { createLiveView, html } from "liveviewjs";
export const helloLiveView = createLiveView({
render: () => html`Hello World!`,
});
Congratulations! You've just created your first LiveView! It doesn't do much yet but let's get it running in the browser.
Setup a new Route
Let's add a route to this LiveView to see it in our browser. Edit packages/express/src/example/index.ts and make the
following highlighted changes:
...
import { htmlPageTemplate, wrapperTemplate } from "./liveViewRenderers";
import { helloLiveView } from "./liveview/hello";
// map request paths to LiveViews
const router: LiveViewRouter = {
"/hello": helloLiveView,
"/autocomplete": autocompleteLiveView,
...
Great! We've now setup our new LiveView to be served at the /hello path. Let's start the server and see it in action.
Start the Express Server
First, load the NPM dependencies:
# install the NPM dependencies
npm install
Then, start the express server:
# start express server
npm run start -w packages/express
You will probably see a warning from NodeJS about using an experimental feature:
ExperimentalWarning: The Fetch API is an experimental feature. This feature could change at any time
(Use `node --trace-warnings ...` to show where the warning was created)
The feature we are using is the built-in fetch method. Feel free to ignore this warning.
See the LiveView in Action
Point your browser to http://localhost:4001/hello, and you should see something like the
following: 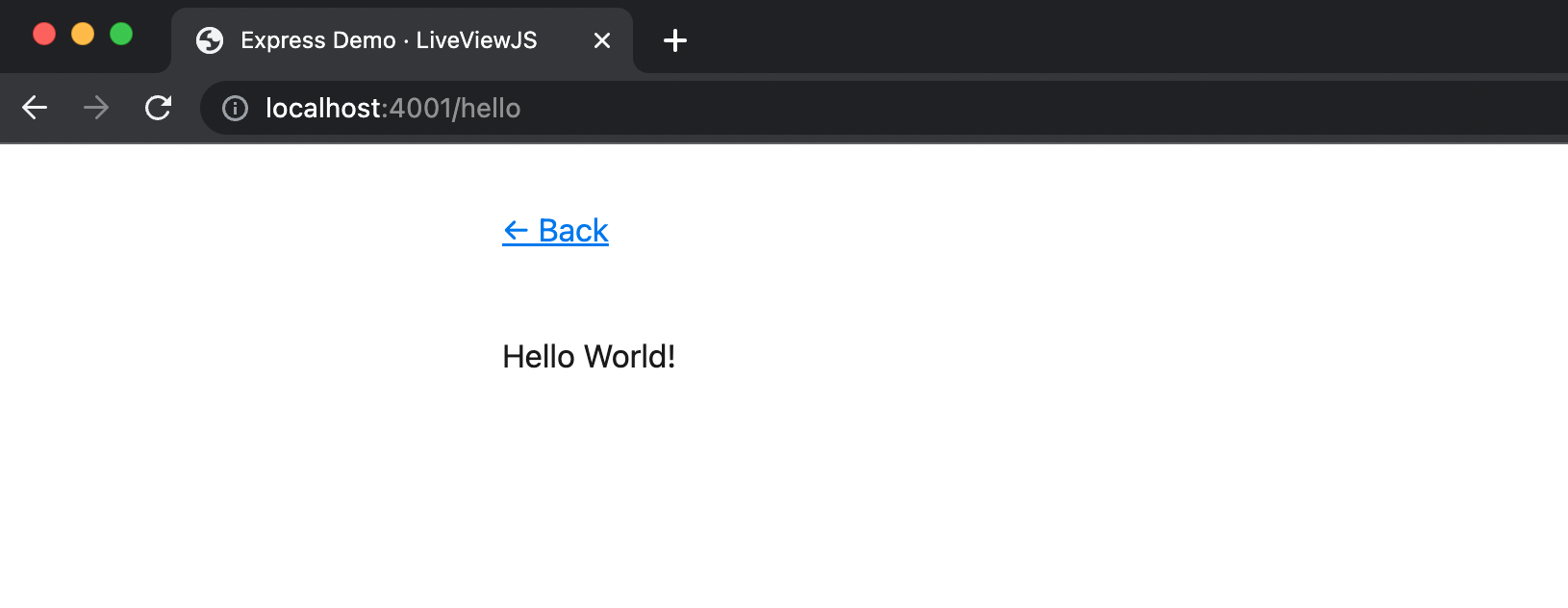
Next Steps
Ok, we got our first LiveView running but it isn't very interactive. Let's make it more interesting by adding a button
that toggles between using text and emojis to say hello. Update the hello.ts file to the following:
import { createLiveView, html } from "liveviewjs";
export const helloLiveView = createLiveView({
mount: (socket) => {
socket.assign({ useEmoji: false });
},
handleEvent(event, socket) {
socket.assign({ useEmoji: !socket.context.useEmoji });
},
render: (context) => {
const msg = context.useEmoji ? "👋 🌎" : "Hello World";
return html`
${msg}
<br />
<button phx-click="toggle">Toggle Message</button>
`;
},
});
Now, when you refresh the page, you should see a button that toggles between using text and emojis to say hello. It should look something like this:
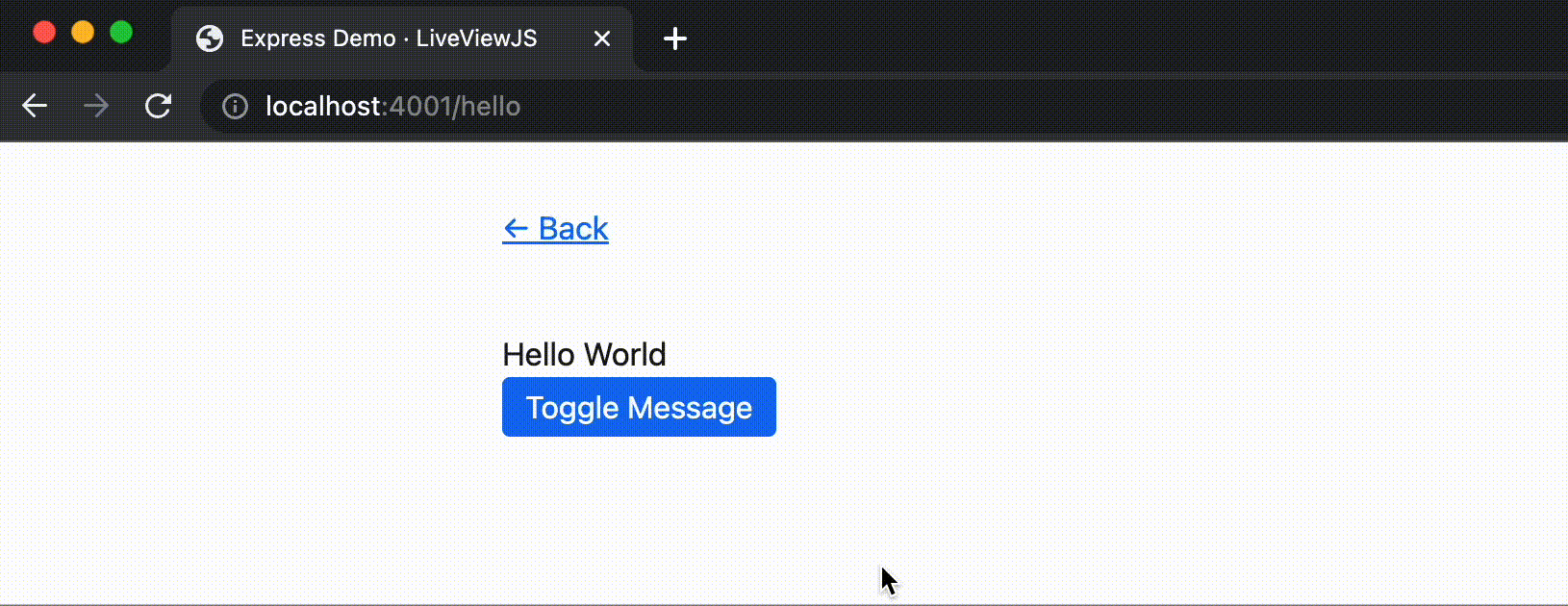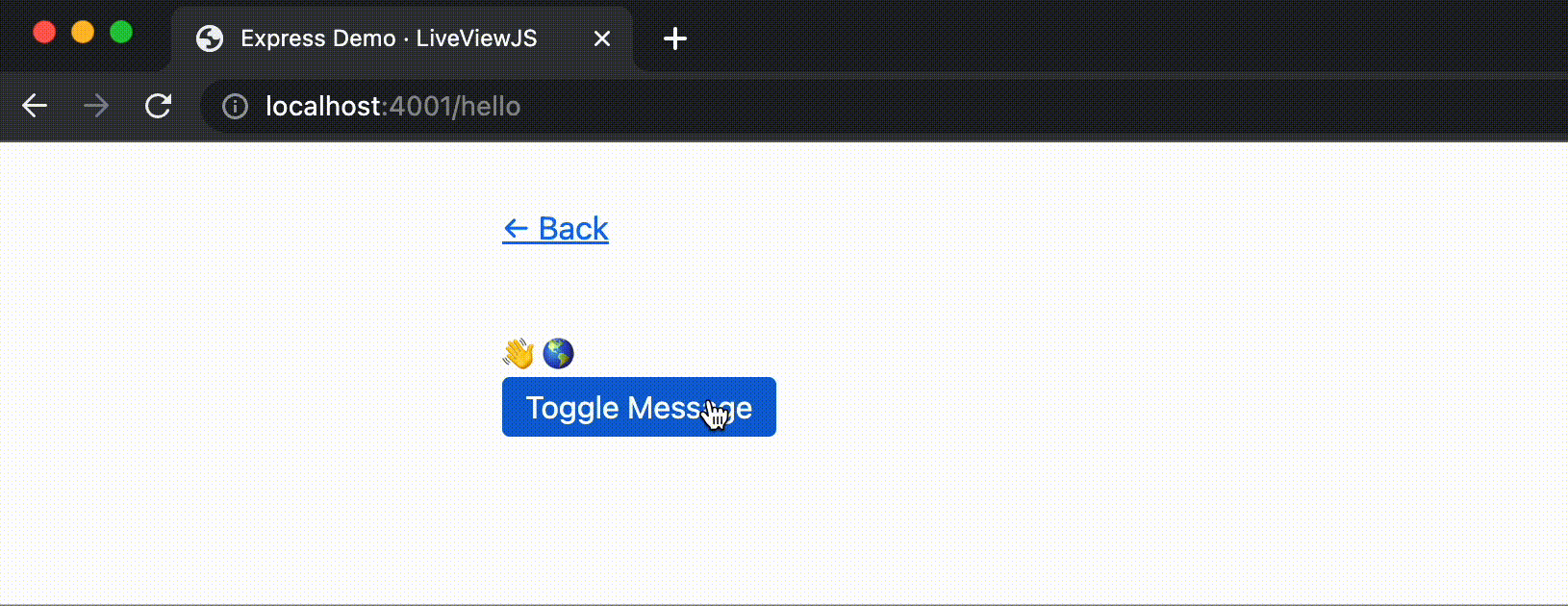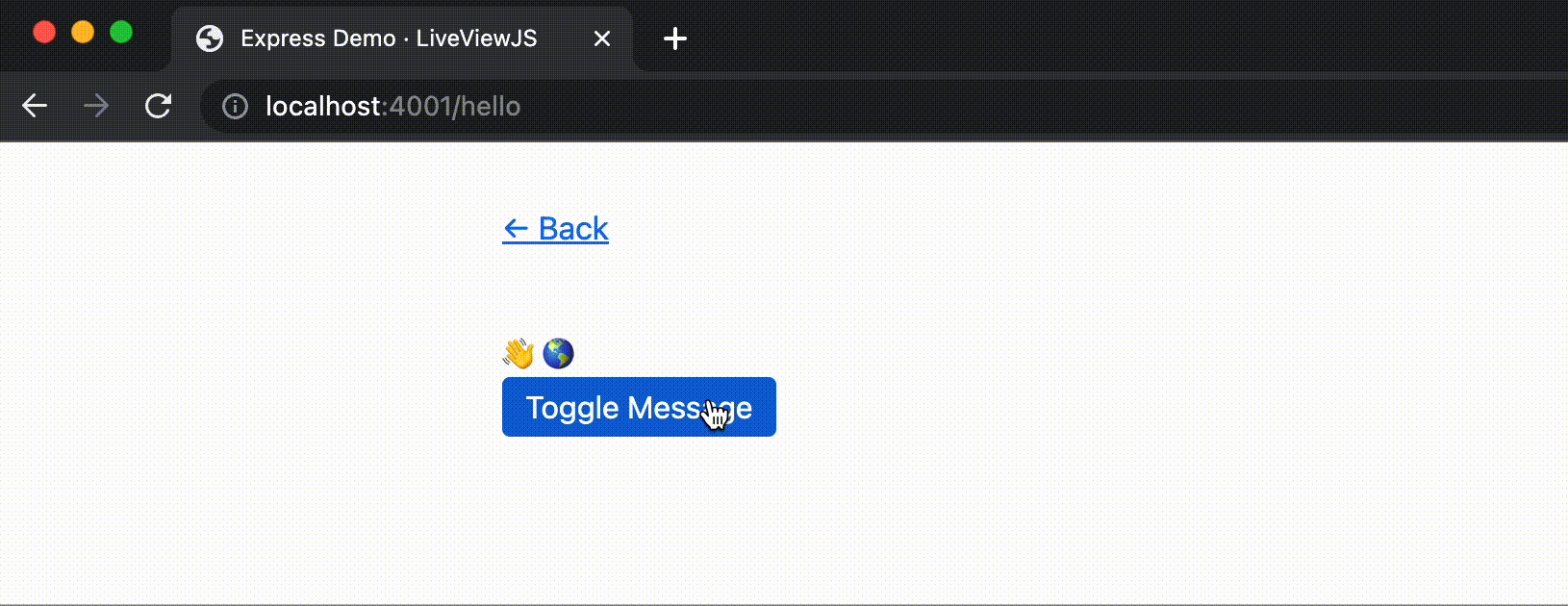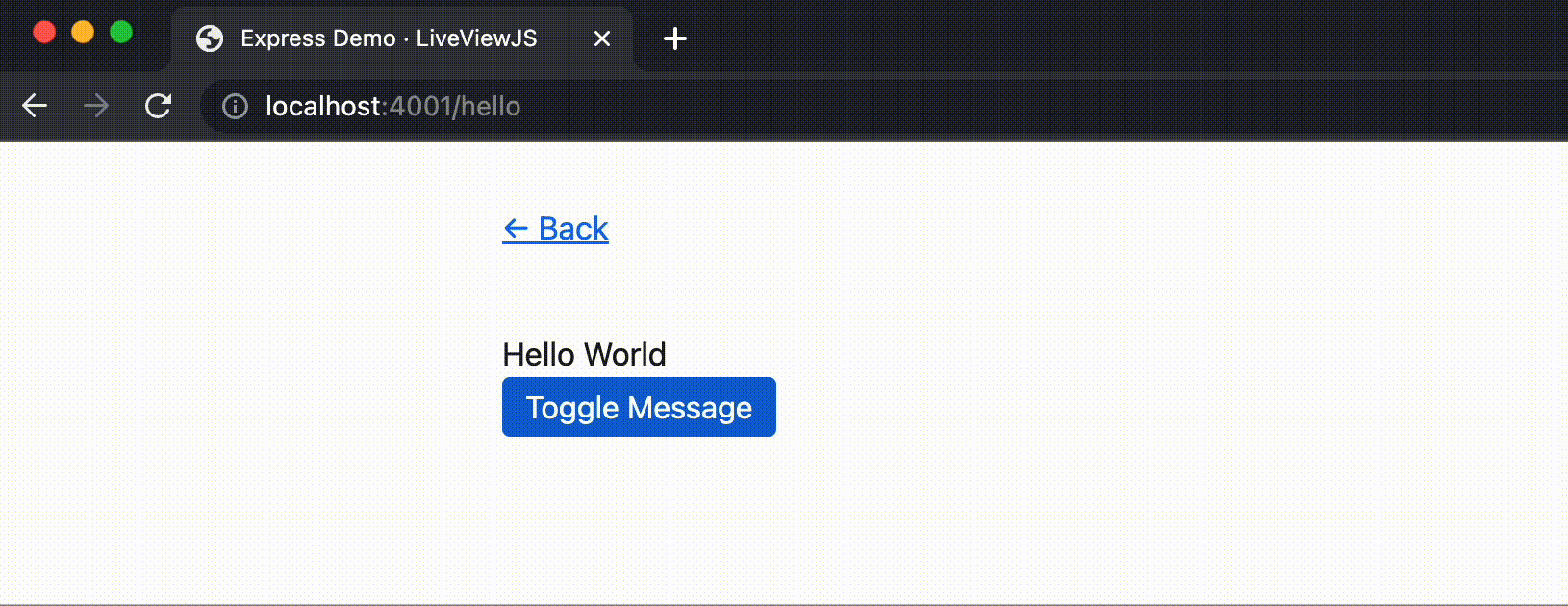
You'll notice that LiveViewJS automatically rebuilds and reloads the server when you make changes to your LiveView code. This is a great way to iterate quickly on your LiveView.
Great start!
You've just created your first LiveView and added it to your webserver! There is a lot more to learn about LiveViewJS but you are well on your way. We recommend you continue to the Anatomy of a LiveView section to start to learn more about how LiveViews work.